Understanding Gonorrhea and Antimicrobial Resistance
Gonorrhea: A Bacterial STD
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the Neisseria gonorrhea bacteria. It can affect the genitals, rectum, and throat. Symptoms can vary by gender, with women often experiencing mild or no symptoms. In men, symptoms include a burning sensation during urination, discharge, and pain or swelling in the testicles.
Antimicrobial Resistance and Gonorrhea Treatment
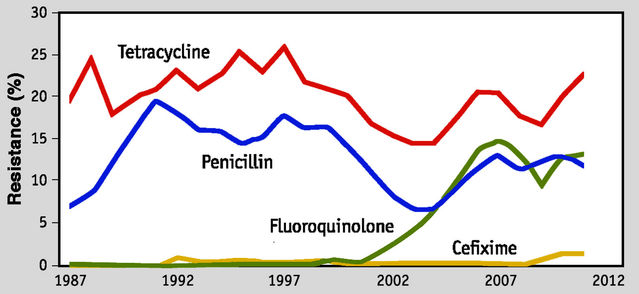
Antibiotics are typically used to treat gonorrhea. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern. The European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported a significant increase in resistance to azithromycin, a common antibiotic used for gonorrhea treatment. Resistance to other antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, has also been observed.
Consequences of Antimicrobial Resistance in Gonorrhea
Antimicrobial resistance can make it more difficult and costly to treat gonorrhea, potentially leading to increased cases and more severe complications. It can also contribute to the spread of other bacterial infections.
Preventing the Spread of STDs
To prevent the spread of STDs, including gonorrhea, it is recommended to: * Abstain from sex or limit the number of sexual partners * Use condoms correctly and consistently during every sexual encounter * Get regular STD screenings * Be aware of the symptoms of STDs and seek medical attention if any symptoms are noticed * Reduce stigma surrounding STDs to encourage individuals to seek treatment and prevent the spread of infection
Addressing the Complexities of STD Prevention
Beyond promoting safe sex practices, it is important to address other factors that contribute to the rise in STD cases, such as: * Improving access to STD services and diagnostic testing * Reducing stigma and promoting open communication about sexual health * Addressing socioeconomic disparities that impact access to healthcare
Conclusion
Gonorrhea remains a prevalent STD worldwide. Antimicrobial resistance poses a significant threat to its treatment. By understanding the causes and consequences of antimicrobial resistance and implementing effective prevention strategies, we can work towards reducing the burden of STDs and safeguarding public health.